Building a Data-Literate Insurance Workforce: Strategies for CDOs
Data literacy has become a critical skill for insurance professionals at all levels. As Chief Data Officers (CDOs) in the insurance industry, one of the most crucial challenges is fostering a data-literate workforce capable of leveraging data for better decision-making and innovation. This blog post explores strategies for CDOs to build and maintain a data-literate insurance workforce, highlighting real-world examples and addressing common challenges.
The Data Literacy Imperative in Insurance
The importance of data literacy in insurance cannot be overstated. A study by Gartner found that by 2023, data literacy will become an explicit and necessary driver of business value, demonstrated by its formal inclusion in over 80% of data and analytics strategies and change management programs [1]. For insurers, this translates to improved risk assessment, more personalized customer experiences, and more efficient operations.
Real-World Examples of Data Literacy Programs in Insurance
While specific, detailed information about data literacy programs in individual insurance companies is not readily available in public sources, we can discuss broader industry trends and general approaches to building data literacy in the insurance sector.
According to a Gartner report, by 2023, data literacy is expected to become an explicit and necessary driver of business value, prompting increased adoption of data literacy initiatives across industries, including insurance [2].
Some general approaches that insurance companies are taking to improve data literacy include:
Tiered Learning Programs: Offering different levels of data education, from basic awareness for all employees to advanced analytics for specialists.
Integration with Business Processes: Embedding data literacy training into day-to-day operations and decision-making processes.
Collaboration Between Data Specialists and Business Units: Encouraging knowledge sharing and practical application of data skills.
Online Learning Platforms: Utilizing e-learning modules to provide flexible, scalable training options.
Data Governance Education: Ensure employees understand the importance of data quality, privacy, and ethical data use.
A survey by Accenture found that 81% of insurers acknowledge that the majority of their workforce will be required to collaborate with AI in the next two years, underlining the growing importance of data literacy [3].
While specific examples of data literacy programs from insurance companies are hard to find, we can look at broader corporate initiatives. Airbnb's Data University is often cited as a successful data literacy initiative in the corporate world [4].
As the insurance industry continues to digitize, more companies will likely develop and publicize their data literacy programs. CDOs in the insurance sector can draw inspiration from these general trends and examples from other industries to develop programs tailored to their specific needs.
Challenges in Building Data Literacy
Varied Skill Levels: Insurance workforces often have a wide range of data literacy skills, from data scientists to claims adjusters with limited data experience.
Resistance to Change: Many insurance professionals are accustomed to traditional methods and may resist adopting data-driven approaches.
Complexity of Insurance Data: Insurance data is often complex and spread across multiple systems, making it challenging to integrate and analyze.
Regulatory Constraints: Insurance's highly regulated nature can complicate data usage and sharing.
Strategies for CDOs to Build Data Literacy
Develop a Comprehensive Data Literacy Program. Create a structured program that caters to different skill levels and job roles. Accenture suggests that effective data literacy programs should cover four key areas: data fundamentals, data analysis, data visualization, and data ethics [5].
Foster a Data-Driven Culture. Encourage a culture where data-driven decision-making is valued and rewarded. McKinsey reports that companies with a strong data culture are 3x more likely to outperform their peers [6] significantly.
Implement Hands-On Training. Provide practical, hands-on training using real insurance scenarios. A study by the Data Literacy Project found that 45% of employees prefer hands-on training for developing data skills [7].
Leverage Internal Experts. Identify and leverage internal data experts to mentor others. This peer-to-peer learning can be highly effective and helps to contextualize data skills within the organization.
Invest in User-Friendly Data Tools. Implement intuitive data visualization and analysis tools that make it easier for non-technical staff to work with data. Gartner predicts that by 2025, 80% of organizations seeking to scale digital business will fail because they do not take a modern approach to data and analytics governance [8].
Establish Data Literacy Success Metrics. Define and track metrics to measure the progress of your data literacy initiatives. These could include the number of employees completing data literacy programs, improvements in data-driven decision-making, or increases in the use of data analytics tools.
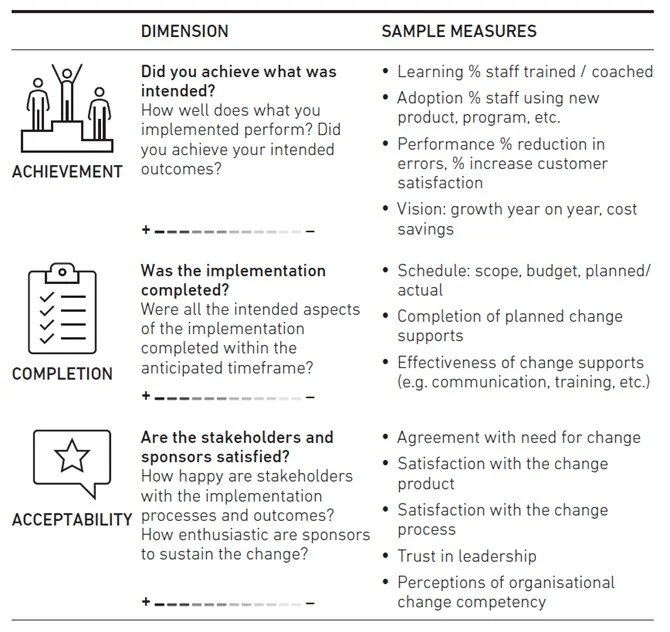
From Driving Data Projects: Example Success Measures
See how the project and change management measures blend in the table above? Specific success measures for a change project focus on engagement, development and adoption. The list here is just an example and not exhaustive.
Addressing the Controversy: Privacy Concerns in Data Literacy
As insurers push for greater data literacy and usage, concerns about data privacy and ethical use of customer information have grown. A survey by Accenture found that 86% of insurance executives agree that organizations must train their employees about the responsible use of AI and data or face consumer backlash [9].
CDOs must ensure that data literacy programs include strong components on data ethics, privacy, and regulatory compliance. This not only addresses potential concerns but also builds trust with customers and regulators.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Data Literacy in Insurance
As we look to the future, the importance of data literacy in insurance will only grow. Emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain will generate even more data, requiring an increasingly sophisticated level of data literacy from insurance professionals.
Moreover, as customers become more data-savvy themselves, insurers will need to be able to communicate complex data concepts clearly and ethically. The insurers who invest in building a data-literate workforce now will be best positioned to thrive in this data-driven future.
Conclusion: Data Literacy as a Competitive Advantage
Building a data-literate insurance workforce is not just about teaching employees to read charts or run analyses. It's about creating a culture where data is understood, valued, and effectively used to drive better outcomes for the business and its customers.
As a CDO, your role in fostering this data-literate culture is crucial. By implementing comprehensive data literacy programs, fostering a data-driven culture, and addressing key challenges, you can help your organization harness the full power of its data assets.
What strategies have you found effective in building data literacy in your organization? How are you addressing the challenges of creating a data-literate workforce in the complex world of insurance? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below.
References
[1] Gartner. (2019). Gartner Says 80% of Organizations Will Fail to Scale Digital Business Due to Lack of Data Literacy Programs by 2025. https://www.gartner.com/en/articles/choose-adaptive-data-governance-over-one-size-fits-all-for-greater-flexibility
[2] Gartner. (2019). Gartner Says By 2023, Data Literacy Will Become an Explicit and Necessary Driver of Business Value. https://tdwi.org/articles/2022/02/04/bi-all-changing-value-of-data-and-need-for-data-literacy.aspx
[3] Accenture. (2021). Technology Vision for Insurance 2021. https://www.accenture.com/us-en/insights/insurance/technology-vision-insurance-2021
[4] Feng, J. (2017). How Airbnb Democratizes Data Science With Data University, Medium. https://medium.com/airbnb-engineering/how-airbnb-democratizes-data-science-with-data-university-3eccc71e073a
[5] Accenture. (2020). "The Human Impact of Data Literacy." https://www.accenture.com/_acnmedia/PDF-115/Accenture-Human-Impact-Data-Literacy-Latest.pdf
[6] McKinsey & Company. (2019). "Catch them if you can: How leaders in data and analytics have pulled ahead." https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/mckinsey-analytics/our-insights/catch-them-if-you-can-how-leaders-in-data-and-analytics-have-pulled-ahead
[7] Data Literacy Project. (2019). The Human Impact of Data Literacy. https://thedataliteracyproject.org/the-human-impact-of-data-literacy/
[8] Gartner. (2020). Gartner Top 10 Data and Analytics Trends for 2021. https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/gartner-top-10-data-and-analytics-trends-for-2021
[9] Accenture. (2021). Technology Vision for Insurance 2021. https://www.accenture.com/us-en/insights/insurance/technology-vision-insurance-2021